Osteoarthritis vs Rheumatoid Arthritis: Differences and Similarities
Arthritis affects millions worldwide, but not all arthritis is the same. Among the most common types are osteoarthritis (OA) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). While both affect the joints, they differ in causes, symptoms, progression, and treatment. In this blog, we will see the difference between osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, including pictures of rheumatoid arthritis vs osteoarthritis, symptoms, treatments, home remedies, and more.
What Is Osteoarthritis vs Rheumatoid Arthritis?
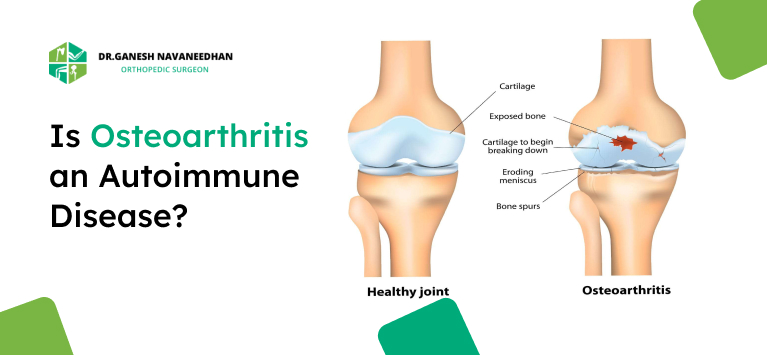
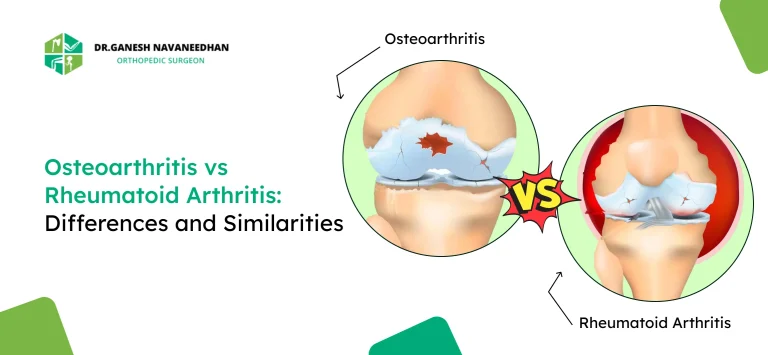
Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common form of arthritis. It happens when the protective cartilage that cushions the ends of your bones wears down over time. This form of arthritis typically affects joints like the knees, hips, and hands.
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disorder. Unlike OA, the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the lining of the joints, causing inflammation and pain. It often affects joints symmetrically, like both wrists or both knees.
Causes of Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis
Osteoarthritis Causes:
- Ageing and joint wear-and-tear
- Obesity
- Joint injuries or overuse
Rheumatoid Arthritis Causes:
- Autoimmune response
- Genetic predisposition
- Environmental triggers like smoking
These causes show how different the origin of these conditions is—mechanical vs immune.
How Do They Feel Like?
OA: Feels like a deep ache in the joints, especially after movement. Pain often worsens by the end of the day.
RA: Feels like a throbbing pain with stiffness, especially in the morning. The pain is often accompanied by fatigue and fever.
How Do They Look Like?
OA: Affected joints may appear enlarged or bony due to bone spurs. Joint deformities may occur over time.
RA: Joints may look swollen and red and feel warm to the touch. Fingers may bend at unusual angles in severe cases.
Pictures of rheumatoid arthritis vs osteoarthritis help in understanding these visible signs.
Who Gets Affected Easily?
Osteoarthritis:
- People over 50
- Individuals with repetitive joint stress (e.g., athletes)
- Those with obesity or prior joint injuries
OA affects 10% of men and 13% of women over 60.
Rheumatoid Arthritis:
- Women aged 30–60
- People with a family history of RA
- Smokers and those exposed to environmental triggers
RA is 2–3 times more common in women than in men.
Understanding who is at risk can help with early detection and management.
OA and RA Differentiation: Key Differences
Here is a quick osteoarthritis vs rheumatoid arthritis chart showing the key differences:
| Feature | Osteoarthritis (OA) | Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) |
| Cause | Wear-and-tear | Autoimmune response |
| Age Group | Older adults | Any age, especially 30–60 |
| Speed of Onset | Gradual | Sudden or gradual |
| Joint Affected | Weight-bearing joints | Symmetrical small joints |
| Morning Stiffness | < 30 mins | > 1 hour |
| Swelling | Mild | Severe |
| Systemic Symptoms | Rare | Common (fatigue, fever) |
| X-Ray Findings | Joint space narrowing, osteophytes | Erosions, bone loss |
This OA and RA differentiation helps to understand the disease better. Knowing the difference between osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis ensures early and correct treatment.
Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis vs Osteoarthritis
While both types cause joint pain and stiffness, they do so differently:
Osteoarthritis Symptoms:
- Joint stiffness after rest
- Pain worsens with activity
- Bony spurs on X-ray
- Reduced joint flexibility
Rheumatoid Arthritis Symptoms:
- Red, swollen joints
- Morning stiffness lasting over an hour
- Fatigue and weight loss
- Symmetrical joint pain
So if you’re asking, “how do I know if I have osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis?” noticing the pattern and duration of stiffness can help. Pictures of rheumatoid arthritis show swollen knuckles, while OA often shows joint deformities over time.
Osteoarthritis vs Rheumatoid Arthritis X-ray Findings
X-rays are crucial in diagnosing both conditions. Let’s look at the osteoarthritis vs rheumatoid arthritis X-ray differences:
OA X-ray: This shows cartilage loss, bone spurs, and joint space narrowing.
RA X-ray: Reveals bone erosion, joint deformities, and reduced bone density.
These pictures of rheumatoid arthritis vs osteoarthritis give visual cues for proper diagnosis.
Which Is Worse: Osteoarthritis or Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Many ask, “which is worse osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis?” The answer depends on severity and personal health. RA tends to progress faster and affects more than just joints—it can impact organs. OA progresses slowly but can cause disability in older adults.
Globally, over 528 million people have osteoarthritis, while 18 million are affected by rheumatoid arthritis. Though RA is less common, it’s often more aggressive. Both conditions can severely impact daily life.
Osteoarthritis vs Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment
Treatments differ based on the cause:
OA Treatment:
- Pain relievers like acetaminophen
- NSAIDs
- Physical therapy
- Joint injections
- Surgery in severe cases
RA Treatment:
- Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs)
- Biologics
- Corticosteroids
- Lifestyle changes
So, when considering osteoarthritis vs rheumatoid arthritis treatment, remember that RA requires immune system control, while OA focuses on joint support and pain relief.
Home Remedies for OA and RA Relief
Here are separate home remedies for each type:
Osteoarthritis Home Remedies:
- Weight loss: Eases pressure on joints.
- Gentle exercise: Strengthens muscles around joints.
- Hot compress: Helps reduce stiffness.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Home Remedies:
- Cold packs: Reduce joint swelling and pain.
- Anti-inflammatory foods: Omega-3-rich fish, leafy greens.
- Mind-body techniques: Meditation, yoga, and stress reduction.
If you wonder, “Do I have rheumatoid arthritis or osteoarthritis?”, try observing how your symptoms respond to these remedies.
Can You Have Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis Together?
Yes, it is possible to have both osteoarthritis (OA) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) at the same time, though it’s uncommon. This condition is called “coexisting arthritis” or “mixed arthritis.” People with one form of arthritis can still develop the other, especially with age or increased joint wear.
OA is due to wear and tear, while RA is autoimmune. Having both can cause more joint pain, stiffness, and movement issues. Diagnosis needs tests and scans. Treatment includes medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes.
Conclusion: Is It Osteoarthritis or Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Understanding whether it’s osteoarthritis vs rheumatoid arthritis is key to managing the condition. OA results from mechanical wear, while RA is driven by immune dysfunction. Treatments, symptoms, and progression differ greatly. With accurate diagnosis, lifestyle changes, and proper medical care, both conditions can be managed effectively.
Whether you’re facing arthritis vs rheumatoid arthritis or asking, “is it osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis?” knowledge is your best defense. Always consult a healthcare provider for personalised advice.
Frequently Asked Questions
OA results from wear and tear; RA is an autoimmune disease. RA also causes systemic symptoms and symmetrical joint pain.
RA causes prolonged morning stiffness, fatigue, and symmetrical pain. OA pain worsens with activity and improves with rest.
RA symptoms include joint redness, fatigue, and swelling. OA causes stiffness, pain with movement, and bone spurs.
Yes, but it is rare. A doctor will run blood tests and imaging for confirmation.
RA usually progresses faster and affects organs, making it more severe in many cases.
Noticing your joint stiffness duration, pain pattern, and systemic symptoms can help identify the type.
RA is a specific autoimmune type of arthritis. Arthritis is the general term for joint inflammation.
Arthritis can be due to many causes; RA is specifically autoimmune and symmetrical.